Struct cbfsshell::ShellMenu
Properties Methods Events Config Settings Errors
The ShellMenu struct enables customizing Shell context menu items and commands.
Syntax
cbfsshell::ShellMenu
Remarks
The ShellMenu struct provides a simple way to create custom context menu items for any items selected in the Windows Shell. An application may add such menu items to perform global or item-specific operations when a user chooses the command in the context menu displayed by the Windows Shell for the selected items.
The struct communicates with the Windows Shell through a proxy DLL that is loaded by Explorer in order to add a custom menu item to context menus and handle invocation of that menu item. The set of modules included in this product is discussed in the Deployment Instructions.
Installation and Initialization
First, call the install method to register the proxy DLL with the Windows Shell. Installation should be done at least once before using the library on a new system, but may be done several times to update the values of the proxy_path and scope properties.
component.Install();
Following the installation, any custom menu items that will be added to the Windows context menu must be registered in the Windows Registry. To do this, call the register_menu_item method for each custom menu item.
component.RegisterMenuItem("MyMenuItem");
NOTE:In Windows 11, additional steps must be taken to make menu items visible in the "main" context menus. See the Shell Menu in Windows 11 section below for more information.
The next step is to call initialize, which will perform the necessary operations to facilitate communication between the system and your code. Initialization only needs to be called once per application launch.
component.Initialize();
Adding Menu Items
Call the activate method to start serving context menu items and begin handling requests from the Windows Shell. After calling activate, the menu_items collection will be populated with the previously registered menu items.
component.Activate();
// If activation was successful this prints out "MyMenuItem"
Console.WriteLine(component.MenuItems[0].Verb);
The Windows Registry only stores the unique text identifiers, or verbs, of the added menu items. As such, their additional properties, such as captions and icons are initialized to their default values every time the menu_items collection is populated. To customize these properties, they must be set manually after calling the activate method, or by handling the on_update_menu event. For example:
component.OnUpdateMenu += (s, e) =>
{
int itemCount = 0;
foreach (MenuItem item in component.MenuItems)
{
if (item != null)
{
item.Caption = "Menu item #" + itemCount;
item.Icon = "shell32.dll,-249"; // icon resource string included with the Windows Shell
itemCount++;
}
}
};
Once the struct is activated, the menu items from the menu_items collection will appear in the File-Explorer's right-click context menu for any selected Windows Shell items.
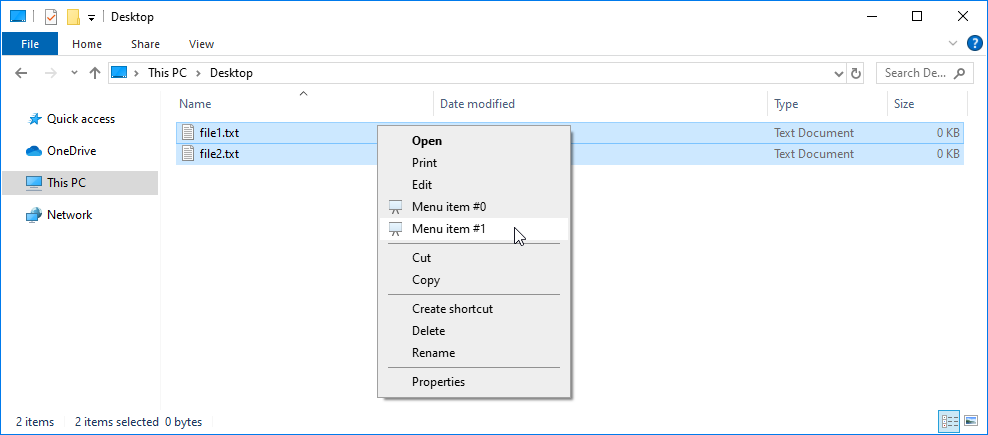
NOTE: Menu items may not be visible in the context menu if their caption property is set to an empty string.
When a user clicks on a context menu item, the on_invoke_menu event is fired, and the selected_items collection is populated with the Windows Shell items selected in Windows File Explorer. An application may use the context provided by the selected_items collection to perform actions specifically tailored to the user's selections. For example:
component.OnInvokeMenu += (s, e) =>
{
if (e.Verb.Equals("MyMenuItem"))
{
Console.WriteLine("Selected items: ");
for (int i = 0; i < component.SelectedItems.Count; i++)
{
SelectedItem item = component.SelectedItems[i];
Console.WriteLine(item.FileName);
}
}
};
Deactivation and Uninstall
To stop handling Windows Shell requests and render all custom menu items inactive, call the deactivate method.
component.Deactivate();
Since the menu items registered via the register_menu_item method are not automatically removed from the Windows Registry, it is recommended to call unregister_menu_item to unregister each menu item individually during the application's uninstall routine.
component.UnregisterMenuItem("MyMenuItem");
Finally, to detach the struct from the Windows Shell and unregister the proxy DLL from the system, call the uninstall method. Normally, this is done when the application is removed from the system.
component.Uninstall();
PIDLs
A PIDL (or an IDL) is a fundamental Windows Shell concept. At a high level, it is pretty simple, as it is just a value that represents a Windows Shell item in the Windows Shell Namespace. It is a bit like a full filesystem path for a physical file or folder, except that it is a binary object and not a string. The name "PIDL" and "IDL" can be used interchangeably. The leading P stands for pointer, the IDL stands for item identifier list, and PIDL generally refers to an IDL itself rather than the pointer to it.
The below information is provided as a general knowledge. Your application will deal with PIDLs only when they denote some Windows Shell items that are not necessarily a part of the Windows Shell namespace extension that you create. Such PIDLs can be used with the Windows Shell API if you decide to call it directly. When CBFS Shell exposes these PIDL values they will appear hex-encoded. If an application needs to call a shell function, it has to decode the PIDL before calling that function.
Just like a full filesystem path is a list of strings separated by the directory separator (on Windows, it is the \ (backslash) character), a PIDL is a list (L is for list) of Ids (identifiers). Unlike a filesystem path, though, a PIDL is binary, and Ids are separated by a special PIDL separator (two consecutive zero bytes).
Microsoft provides more details about PIDLs here Identifying Namespace Objects.
Verbs
The ShellMenu struct is built so that one Explorer command with one GUID is registered in the registry. Verbs are used to identify individual menu items.
A verb is an alphanumeric string that identifies a menu item. Use verbs specific to your application to avoid collisions with other applications. For example, generic words "open" or "edit" are inappropriate because they are or may be used by the Windows Shell or other applications, while "OpenWithMyFineTool" should be ok, as long as "MyFineTool" is not generic.
Each menu item with a distinct verb must be registered before it can be used. This is done by creating the corresponding keys in the registry. Registration is done using the register_menu_item. To remove an item, use unregister_menu_item.
Shell Menu in Windows 11
In Windows 11, menu commands by default appear only in the secondary menu that is shown when you choose "More Options" in the context menu. Windows 11, with its redesigned Shell, and the ShellMenu struct support adding one main menu item into the main context menu of Windows 11 Shell.
For this, the menu item (command) and its GUID should be declared in a sparse package manifest that is then converted to a sparse package file. A separate manifest and sparse package file is required for each supported processor architecture.
The sparse package manifest you prepare should include the block similar to the following:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<Package
...
xmlns:desktop4="http://schemas.microsoft.com/appx/manifest/desktop/windows10/4"
xmlns:desktop5="http://schemas.microsoft.com/appx/manifest/desktop/windows10/5"
xmlns:uap="http://schemas.microsoft.com/appx/manifest/uap/windows10"
xmlns:com="http://schemas.microsoft.com/appx/manifest/com/windows10"
IgnorableNamespaces="uap uap2 uap3 rescap desktop desktop4 desktop5 uap10 com">
<Identity Name="<your-package-name-here>" ProcessorArchitecture="..." Publisher="CN=<your-certificate-common-name-here>" Version="1.0.0.0" />
...
<Applications>
<Application Id="<your-app-id-here>" Executable="..." uap10:TrustLevel="mediumIL" uap10:RuntimeBehavior="win32App">
<Extensions>
<desktop4:Extension Category="windows.fileExplorerContextMenus">
<desktop4:FileExplorerContextMenus>
<desktop5:ItemType Type="*">
<desktop5:Verb Id="<your-verb-here>" Clsid="<your-command-guid-here>" />
</desktop5:ItemType>
</desktop4:FileExplorerContextMenus>
</desktop4:Extension>
<com:Extension Category="windows.comServer">
<com:ComServer>
<com:SurrogateServer DisplayName="Context menu verb handler">
<com:Class Id="<your-command-guid-here>" Path="CBFSShell.<Id>.<processor-architecture-here>.dll" ThreadingModel="STA"/>
</com:SurrogateServer>
</com:ComServer>
</com:Extension>
</Extensions>
</Application>
</Applications>
</Package>
- "<your-verb-here>" should be replaced with the verb of the menu command. It should be used by the system to tell the command handler, which command was invoked, however, at least on some systems, this doesn't work right. Due to this bug, only one main menu item is currently supported.
- "<your-command-guid-here>" should be replaced with the command GUID. This value can be obtained using the CommandGUID configuration setting. Note that the value in the manifest should not include curly brackets, whereas the configuration setting returns a value in the standard registry format with curly brackets. Several menu items (commands) in one sparse package manifest are possible, but require different command GUIDs, which in turn require proxy DLLs with different license IDs.
- "<processor-architecture-here>" should be replaced with the processor architecture, for which the sparse package manifest is prepared. It can be "x86", "x64", or "ARM64".
- "CBFSShell.<Id>.<processor-architecture-here>.dll" will look similar to "CBFSShell.12345678.x64.dll", where "12345678" should be replaced by your real proxy Id or "TRIAL", and the processor architecture is described above.
- "<your-certificate-common-name-here>" is the value of the Subject CN ("Common Name") field of the code signing certificate that is used to sign the application and the package.
Registration and unregistration of such a manifest are normally done via WinRT APIs, which are not easy to use from non-.NET applications. To assist with the complications, the struct supports registration and unregistration of an application-provided manifest when the application calls install and uninstall respectively. To make use of this assistance, the application must set two configuration settings: SparsePackageFile (contains the path to the package file) and SparsePackageName (contains the name of the package, "<your-package-name-here>" in the above snippet). Note that SparsePackageFile must point not at the manifest but at the prepared and signed sparse package file (see below).
In addition to the sparse package manifest and file, one more step is required. Next to the application EXE, there must be the <application>.exe.manifest present with the following content:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<assembly manifestVersion="1.0" xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:asm.v1">
<assemblyIdentity version="0.0.0.1" name="<your-app-name-here>.app"/>
<msix xmlns="urn:schemas-microsoft-com:msix.v1" publisher="CN=<your-certificate-common-name-here>" packageName="<your-package-name-here>" applicationId="<your-app-id-here>"/>
</assembly>
- "<your-package-name-here>" in this manifest must match with the corresponding value of the sparse file manifest.
- "<your-app-id-here>" in this manifest must match with the corresponding value of the sparse file manifest.
- The "CN" value ("<your-certificate-common-name-here>") comes from your code signing certificate. This value must match the corresponding value in the sparse file manifest.
The sparse package manifest should be converted into a sparse package file. This is done by running two commands:
makeappx.exe pack /d <directory-with-manifest> /p <your-app-name-here>.msix /nv
signtool.exe sign /fd SHA256 /a /n "<your-certificate-common-name-here>" <your-app-name-here>.msix
or
signtool.exe sign /fd SHA256 /a /f "<your-certificate-file-name-here>.pfx" /p <certificate-password-here>
Both tools come from Windows SDK. makeappx.exe creates the sparse file package from the manifest, and signtool.exe signs it.
Signtool takes a certificate either from the Personal/My certificate storage in your system (the common name is used for selecting the correct certificate) or from a specified PFX file. A file can be used in development/test scenarios, whereas production code signing certificates usually come on hardware and are reachable via the Windows Certificate Store.
The sparse package manifest should reside in a subdirectory, as the makeappx.exe accepts a directory with the manifest as a parameter. The manifest for each processor architecture should reside in its own subdirectory, as it is converted to a signed package separately.
Troubleshooting
Following are some helpful resources for troubleshooting issues related to the display of menu items.
- If you are developing your application and you stop and start repeatedly while keeping Windows File Explorer open, there may be a memory/cache issue. To avoid this situation one should terminate Explorer and reopen it.
- If your context menu items do not appear at all or an excess number of menu items appear, this may indicate a registration/deregistration issue. Try running the application with administrative privileges.
- If you are seeing strange behavior not contained in this list, please reach out to us with a description of the problem and we are happy to help. Our support team is available over email at support@callback.com
Object Lifetime
The new() method returns a mutable reference to a struct instance. The object itself is kept in the global list maintainted by CBFSShell. Due to this, the ShellMenu struct cannot be disposed of automatically. Please, call the dispose(&mut self) method of ShellMenu when you have finished using the instance.
Property List
The following is the full list of the properties of the struct with short descriptions. Click on the links for further details.
| menu_items_count | The number of records in the MenuItem arrays. |
| menu_item_caption | Specifies the menu item's caption. |
| menu_item_enabled | Specifies that a menu item is enabled. |
| menu_item_flags | Flags of the item. |
| menu_item_icon | Specifies the icon of the menu item. |
| menu_item_verb | A verb (text identifier) of the item. |
| menu_item_visible | Specifies that a menu item is visible. |
| proxy_path | Specifies the path to the native proxy DLL. |
| scope | Specifies whether the struct is registered for the current user or for all users. |
| selected_items_count | The number of records in the SelectedItem arrays. |
| selected_item_file_name | Contains a file name of the selected item. |
| selected_item_id | Contains an Id of the selected item. |
| selected_item_pidl | Contains a PIDL of the selected item. |
Method List
The following is the full list of the methods of the struct with short descriptions. Click on the links for further details.
| activate | Tells the struct to start handling the requests sent to the namespace extension. |
| config | Sets or retrieves a configuration setting. |
| deactivate | Tells the struct to stop handling the requests sent to the extension handler. |
| initialize | Initializes the core library. |
| install | Registers context menu information to the system. |
| register_menu_item | Adds a menu item to the Windows Registry. |
| uninstall | Unregisters context menu information from the system. |
| unregister_menu_item | Unregisters a previously registered menu item. |
Event List
The following is the full list of the events fired by the struct with short descriptions. Click on the links for further details.
| on_error | Fires when an unhandled error occurs during an event. |
| on_invoke_menu | Fires when an item of the context menu is invoked. |
| on_update_menu | Fires when the context menu needs to be updated. |
Config Settings
The following is a list of config settings for the struct with short descriptions. Click on the links for further details.
| CanonicalName | A human-readable name of the command. |
| CommandGUID | A GUID of the Explorer command. |
| IPCFormat | The fixed name of the RPC endpoint. |
| IsInstalled | Specifies whether the installation was performed. |
| ProductGUID | ID of the proxy DLL. |
| ServerStartArguments | The arguments to pass with the server start command. |
| ServerStartCommandLine | The command line to run when the server is not available. |
| ServerStartOperation | The operation verb. |
| ServerStartShowOption | Defines how the application windows should be shown. |
| ServerStartTimeToWait | Optional time to wait before trying to connect to the RPC server after starting it. |
| ServerStartWorkingDirectory | The working directory. |
| SparsePackageFile | The path to the sparse package file. |
| SparsePackageName | The name of the sparse package. |
| BuildInfo | Information about the product's build. |
| LicenseInfo | Information about the current license. |
menu_items_count property (ShellMenu Struct)
The number of records in the MenuItem arrays.
Syntax
fn menu_items_count(&self ) -> Result<i32, CBFSShellError>
Default Value
0
Remarks
This property controls the size of the following arrays:
The array indices start at 0 and end at menu_items_count - 1.This property is read-only.
Data Type
i32
menu_item_caption property (ShellMenu Struct)
Specifies the menu item's caption.
Syntax
fn menu_item_caption(&self , MenuItemIndex : i32) -> Result<String, CBFSShellError>
fn set_menu_item_caption(&self, MenuItemIndex : i32, value : &str) -> Option<CBFSShellError> fn set_menu_item_caption_ref(&self, MenuItemIndex : i32, value : &String) -> Option<CBFSShellError>
Default Value
""
Remarks
Specifies the menu item's caption.
This field contains the caption or title of the menu item - the text of the item, visible to a user.
The MenuItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the MenuItemsCount property.
Data Type
String
menu_item_enabled property (ShellMenu Struct)
Specifies that a menu item is enabled.
Syntax
fn menu_item_enabled(&self , MenuItemIndex : i32) -> Result<bool, CBFSShellError>
fn set_menu_item_enabled(&self, MenuItemIndex : i32, value : bool) -> Option<CBFSShellError>
Default Value
true
Remarks
Specifies that a menu item is enabled.
This field specifies whether the menu item is enabled and can be selected by a user.
The MenuItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the MenuItemsCount property.
Data Type
bool
menu_item_flags property (ShellMenu Struct)
Flags of the item.
Syntax
fn menu_item_flags(&self , MenuItemIndex : i32) -> Result<i32, CBFSShellError>
fn set_menu_item_flags(&self, MenuItemIndex : i32, value : i32) -> Option<CBFSShellError>
Default Value
0
Remarks
Flags of the item.
This field is a combination of zero or more flags that specify the attributes of the menu item. The possible flags include:
| CMF_DEFAULT | 0x00 | No command flags are set |
| CMF_HAS_SUBCOMMANDS | 0x01 | Not used. |
| CMF_HASSPLITBUTTON | 0x02 | A split button is displayed. |
| CMF_HIDELABEL | 0x04 | The label is hidden. |
| CMF_ISSEPARATOR | 0x08 | The command is a separator.
In Windows 11, a separator is properly displayed in the Classic menu, but the new context menu of Windows 11 ignores this flag and does not properly display separator items. |
| CMF_HASLUASHIELD | 0x0010 | A UAC shield is displayed. |
| CMF_ISDROPDOWN | 0x0080 | Selecting the command opens a drop-down submenu. |
| CMF_TOGGLEABLE | 0x0100 | The item is a switch. |
The MenuItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the MenuItemsCount property.
Data Type
i32
menu_item_icon property (ShellMenu Struct)
Specifies the icon of the menu item.
Syntax
fn menu_item_icon(&self , MenuItemIndex : i32) -> Result<String, CBFSShellError>
fn set_menu_item_icon(&self, MenuItemIndex : i32, value : &str) -> Option<CBFSShellError> fn set_menu_item_icon_ref(&self, MenuItemIndex : i32, value : &String) -> Option<CBFSShellError>
Default Value
""
Remarks
Specifies the icon of the menu item.
The field may be set to an icon resource string in the standard format, for instance "shell32.dll,-249". When set, this icon will be displayed next to the menu item caption.
The MenuItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the MenuItemsCount property.
Data Type
String
menu_item_verb property (ShellMenu Struct)
A verb (text identifier) of the item.
Syntax
fn menu_item_verb(&self , MenuItemIndex : i32) -> Result<String, CBFSShellError>
Default Value
""
Remarks
A verb (text identifier) of the item.
This field contains a Verb, which is a unique text identifier of the item. If a menu item is a child item, this value of this field is <ParentVerb>::<Verb>.
The MenuItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the MenuItemsCount property.
This property is read-only.
Data Type
String
menu_item_visible property (ShellMenu Struct)
Specifies that a menu item is visible.
Syntax
fn menu_item_visible(&self , MenuItemIndex : i32) -> Result<bool, CBFSShellError>
fn set_menu_item_visible(&self, MenuItemIndex : i32, value : bool) -> Option<CBFSShellError>
Default Value
true
Remarks
Specifies that a menu item is visible.
This field specifies whether the menu item is visible and can be seen by a user.
The MenuItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the MenuItemsCount property.
Data Type
bool
proxy_path property (ShellMenu Struct)
Specifies the path to the native proxy DLL.
Syntax
fn proxy_path(&self ) -> Result<String, CBFSShellError>
fn set_proxy_path(&self, value : &str) -> Option<CBFSShellError> fn set_proxy_path_ref(&self, value : &String) -> Option<CBFSShellError>
Default Value
""
Remarks
This property may be used to specify the path to the native proxy DLL, which is loaded by the Windows Shell. The value may be in one of the following formats:
- A directory path containing proxy DLLs. For example: C:\Users\User\Documents\CBFS Shell 2024\proxy. In this case, the struct will automatically choose the first DLL with the appropriate architecture.
- A full file path with wildcards in the filename. For example C:\Users\User\Documents\CBFS Shell 2024\proxy\CBFSShell.*.x64. In this case, the struct will automatically choose the first DLL that matches the specified pattern.
If left empty, the struct will automatically attempt to locate the appropriate DLL by searching the directory where the application's executable resides.
Data Type
String
scope property (ShellMenu Struct)
Specifies whether the struct is registered for the current user or for all users.
Syntax
fn scope(&self ) -> Result<i32, CBFSShellError>
fn set_scope(&self, value : i32) -> Option<CBFSShellError>
Possible Values
0 // AllUsers
1 // CurrentUser
Default Value
1
Remarks
This property specifies whether the information related to the struct is written to the registry for the current user or for all users.
The values are
| isAllUsers (0) | All users. |
| isCurrentUser (1, default) | Current user. |
If information is to be written for all users, administrative rights are required to successfully execute the install and uninstall methods. If the user account of the process that calls these methods does not have such rights, the call will fail with an error.
Data Type
i32
selected_items_count property (ShellMenu Struct)
The number of records in the SelectedItem arrays.
Syntax
fn selected_items_count(&self ) -> Result<i32, CBFSShellError>
Default Value
0
Remarks
This property controls the size of the following arrays:
The array indices start at 0 and end at selected_items_count - 1.This property is read-only.
Data Type
i32
selected_item_file_name property (ShellMenu Struct)
Contains a file name of the selected item.
Syntax
fn selected_item_file_name(&self , SelectedItemIndex : i32) -> Result<String, CBFSShellError>
Default Value
""
Remarks
Contains a file name of the selected item.
If an item is a filesystem object and its PIDL can be resolved to a filesystem path, this field contains a full path on the filesystem; otherwise, the field is empty.
The SelectedItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the SelectedItemsCount property.
This property is read-only.
Data Type
String
selected_item_id property (ShellMenu Struct)
Contains an Id of the selected item.
Syntax
fn selected_item_id(&self , SelectedItemIndex : i32) -> Result<String, CBFSShellError>
Default Value
""
Remarks
Contains an Id of the selected item.
If a selected item comes from within the virtual Windows Shell folder managed by the ShellFolder struct, this field contans an application-defined Id. In other cases, this field is empty and the application may use the PIDL field to identify the item.
The SelectedItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the SelectedItemsCount property.
This property is read-only.
Data Type
String
selected_item_pidl property (ShellMenu Struct)
Contains a PIDL of the selected item.
Syntax
fn selected_item_pidl(&self , SelectedItemIndex : i32) -> Result<Vec<u8>, CBFSShellError>
Remarks
Contains a PIDL of the selected item.
This field contains the PIDL of the selected item.
The SelectedItemIndex parameter specifies the index of the item in the array. The size of the array is controlled by the SelectedItemsCount property.
This property is read-only.
Data Type
Vec
activate method (ShellMenu Struct)
Tells the struct to start handling the requests sent to the namespace extension.
Syntax
fn activate(&self) -> Result<(), CBFSShellError>
Remarks
This method is used to tell the struct to begin handling Windows Shell requests and start firing the corresponding events.
Customizing Menu Items
When activate is called to start handling Windows Shell requests the first time after the application is launched, the menu_items collection gets populated with the menu items, registered in the Windows Registry. The items in the menu_items collection initially don't contain any values in their properties except for Verb and ParentVerb. An application should fill those items' properties either right after using the activate method or dynamically, in response to the on_update_menu event.NOTE: Registered menu items may not appear in the context menu if their Caption property is set to an empty string.
Menu Item Persistence
When the deactivate method is called to stop the struct, registered menu items will remain in the menu_items list. If the struct is restarted by calling this method after deactivation, the properties of these menu items will not need to be repopulated.config method (ShellMenu Struct)
Sets or retrieves a configuration setting.
Syntax
fn config(&self, configuration_string : &str) -> Result<String, CBFSShellError>
Remarks
config is a generic method available in every struct. It is used to set and retrieve configuration settings for the struct.
These settings are similar in functionality to properties, but they are rarely used. In order to avoid "polluting" the property namespace of the struct, access to these internal properties is provided through the config method.
To set a configuration setting named PROPERTY, you must call Config("PROPERTY=VALUE"), where VALUE is the value of the setting expressed as a string. For boolean values, use the strings "True", "False", "0", "1", "Yes", or "No" (case does not matter).
To read (query) the value of a configuration setting, you must call Config("PROPERTY"). The value will be returned as a string.
deactivate method (ShellMenu Struct)
Tells the struct to stop handling the requests sent to the extension handler.
Syntax
fn deactivate(&self) -> Result<(), CBFSShellError>
Remarks
This method tells the struct to stop handling Windows Shell requests and stop firing the corresponding events.
initialize method (ShellMenu Struct)
Initializes the core library.
Syntax
fn initialize(&self) -> Result<(), CBFSShellError>
Remarks
This method initializes the core library and must be called each time the application starts before attempting to use other struct's methods. The only exceptions to this are install, uninstall, register_menu_item, and unregister_menu_item.
If the application explicitly specifies the path to the proxy DLL, it should do this through the proxy_path property before calling this method.
install method (ShellMenu Struct)
Registers context menu information to the system.
Syntax
fn install(&self) -> Result<(), CBFSShellError>
Remarks
This method is used to install the native proxy DLL that integrates with the Windows Shell.
Before calling this method, you may change the default values of the proxy_path, and scope properties. These values are used during installation.
Registry Scope and User Permissions
The scope property specifies whether the information is written to the registry for the current user or for all users.In the latter case, administrative rights are required to execute this method successfully. If the user account of the process that calls this method does not have such rights, the call will fail with an ERROR_PRIVILEGE_NOT_HELD (0x0522) error.
register_menu_item method (ShellMenu Struct)
Adds a menu item to the Windows Registry.
Syntax
fn register_menu_item(&self, verb : &str) -> Result<(), CBFSShellError>
Remarks
This method registers a menu item to the Windows Registry. Menu items must be registered before they can be used in a context menu. Normally, this is only needs to be done once during application installation.
The Verb parameter specifies a unique text identifier of the context menu item, further referred to as Verb. A verb is the only aspect of the menu item that gets stored in the Windows Registry.
It is possible to create a menu item with a submenu that contains child items. Note that only one level of submenus is supported on Windows 11, so the struct limits addition of items to one level of submenus too.
To create a submenu, when adding a child item, set Verb to the format <ParentVerb>::<Verb>, where ParentVerb denotes the menu item that is a parent for a submenu. Note that the parent's verb is used only in this method to specify the parent, and the struct passes just the Verb part to the event handlers. Thus, the verb must be unique across all items added via ShellMenu.
Windows Registry Pollution
Menu items registered with the register_menu_item method are not automatically removed from the Windows Registry. To avoid polluting the Registry, it is recommended to unregister each item before the uninstall method is called.
Customizing Menu Items
When activate is called to start handling Windows Shell requests the first time after the application is launched, the menu_items collection gets populated with the menu items, registered in the Windows Registry. The items in the menu_items collection initially don't contain any values in their properties except for Verb and ParentVerb. An application should fill those items' properties either right after using the activate method or dynamically, in response to the on_update_menu event.NOTE: Registered menu items may not appear in the context menu if their Caption property is set to an empty string.
Registry Scope and User Permissions
The scope property specifies whether the information is written to the registry for the current user or for all users.In the latter case, administrative rights are required to execute this method successfully. If the user account of the process that calls this method does not have such rights, the call will fail with an ERROR_PRIVILEGE_NOT_HELD (0x0522) error.
uninstall method (ShellMenu Struct)
Unregisters context menu information from the system.
Syntax
fn uninstall(&self) -> Result<(), CBFSShellError>
Remarks
This method is used to uninstall the proxy DLL that integrates with the Windows Shell from the system.
Before calling this method, you may change the default value of the scope property.
Windows Registry Pollution
Menu items registered with the register_menu_item method are not automatically removed from the Windows Registry. To avoid polluting the Registry, it is recommended to unregister each item before the uninstall method is called.
Registry Scope and User Permissions
The scope property specifies whether the information is written to the registry for the current user or for all users.In the latter case, administrative rights are required to execute this method successfully. If the user account of the process that calls this method does not have such rights, the call will fail with an ERROR_PRIVILEGE_NOT_HELD (0x0522) error.
Handling multiple structs
As ShellFolder and ShellMenu structs share a proxy DLL and a product GUID, they store some common information in a registry key. Calling the Uninstall method of one of the components will delete a shared registry key as well.
Each struct should be uninstalled properly by calling the corresponding Uninstall method. At the same time, if an application needs to uninstall just one struct and keep the other(s), it should call the Uninstall method of that struct and then call the Install method of the other structs to restore the common information in the shared registry key.
unregister_menu_item method (ShellMenu Struct)
Unregisters a previously registered menu item.
Syntax
fn unregister_menu_item(&self, verb : &str) -> Result<(), CBFSShellError>
Remarks
This method is used to remove a menu item that was registered with register_menu_item from the Windows Registry. This should normally be done once per each menu item after the uninstall method has been called.
The Verb parameter specifies the unique text identifier of the context menu item. If an item is a child in a submenu, this child's own verb is enough (a parent verb should not be specified).
Registry Scope and User Permissions
The scope property specifies whether the information is written to the registry for the current user or for all users.In the latter case, administrative rights are required to execute this method successfully. If the user account of the process that calls this method does not have such rights, the call will fail with an ERROR_PRIVILEGE_NOT_HELD (0x0522) error.
on_error event (ShellMenu Struct)
Fires when an unhandled error occurs during an event.
Syntax
// ShellMenuErrorEventArgs carries the ShellMenu Error event's parameters.
pub struct ShellMenuErrorEventArgs {
fn error_code(&self) -> i32
fn description(&self) -> &String
}
// ShellMenuErrorEvent defines the signature of the ShellMenu Error event's handler function.
pub trait ShellMenuErrorEvent {
fn on_error(&self, sender : ShellMenu, e : &mut ShellMenuErrorEventArgs);
}
impl <'a> ShellMenu<'a> {
pub fn on_error(&self) -> &'a dyn ShellMenuErrorEvent;
pub fn set_on_error(&mut self, value : &'a dyn ShellMenuErrorEvent);
...
}
Remarks
This event fires when an unhandled error occurs. Developers can use this information to track down unhandled errors that occur in the struct.
ErrorCode contains an error code and Description contains a textual description of the error.
on_invoke_menu event (ShellMenu Struct)
Fires when an item of the context menu is invoked.
Syntax
// ShellMenuInvokeMenuEventArgs carries the ShellMenu InvokeMenu event's parameters.
pub struct ShellMenuInvokeMenuEventArgs {
fn verb(&self) -> &String
fn context(&self) -> i64
}
// ShellMenuInvokeMenuEvent defines the signature of the ShellMenu InvokeMenu event's handler function.
pub trait ShellMenuInvokeMenuEvent {
fn on_invoke_menu(&self, sender : ShellMenu, e : &mut ShellMenuInvokeMenuEventArgs);
}
impl <'a> ShellMenu<'a> {
pub fn on_invoke_menu(&self) -> &'a dyn ShellMenuInvokeMenuEvent;
pub fn set_on_invoke_menu(&mut self, value : &'a dyn ShellMenuInvokeMenuEvent);
...
}
Remarks
This event is fired when a user invokes, or clicks on, a context menu item that has been registered with register_menu_item. To obtain the list of the Windows Shell items for which the context menu was displayed, use the selected_items property.
Verb contains the unique text identifier of the menu item that was invoked.
Context is a unique identifier that remains the same across multiple event calls for the same operation. Since the event may fire multiple times for the same operation, its value may be used to avoid performing the same tasks more than once.
UI Considerations
Event handlers are called in the context of threads that run in the MTA (multithreaded apartment) state. This state is not suitable for showing UI elements. Thus, event handlers should create an STA thread and use it to display a needed window. For example:var thread = new Thread(() => { ... } // "..." is the code that an event handler executes in a helper thread
thread.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA);
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
thread.Join(); // optional, if your code should work synchronously
on_update_menu event (ShellMenu Struct)
Fires when the context menu needs to be updated.
Syntax
// ShellMenuUpdateMenuEventArgs carries the ShellMenu UpdateMenu event's parameters.
pub struct ShellMenuUpdateMenuEventArgs {
fn verb(&self) -> &String
fn context(&self) -> i64
}
// ShellMenuUpdateMenuEvent defines the signature of the ShellMenu UpdateMenu event's handler function.
pub trait ShellMenuUpdateMenuEvent {
fn on_update_menu(&self, sender : ShellMenu, e : &mut ShellMenuUpdateMenuEventArgs);
}
impl <'a> ShellMenu<'a> {
pub fn on_update_menu(&self) -> &'a dyn ShellMenuUpdateMenuEvent;
pub fn set_on_update_menu(&mut self, value : &'a dyn ShellMenuUpdateMenuEvent);
...
}
Remarks
This event is fired when the system needs to update the context menu before it is displayed. The event fires separately for each menu item that was registered via register_menu_item. An event handler is expected to update the menu item in the menu_items collection if such an update is required, and such updates will be reflected in the displayed menu. To obtain the list of Windows Shell items for which the context menu is about to be displayed, use the selected_items property.
Verb contains the unique text identifier of the corresponding menu item that may be updated.
Context is a unique identifier that remains the same across multiple event calls for the same operation. Since the event may fire multiple times for the same operation, its value may be used to avoid performing the same tasks more than once.
UI Considerations
Event handlers are called in the context of threads that run in the MTA (multithreaded apartment) state. This state is not suitable for showing UI elements. Thus, event handlers should create an STA thread and use it to display a needed window. For example:var thread = new Thread(() => { ... } // "..." is the code that an event handler executes in a helper thread
thread.SetApartmentState(ApartmentState.STA);
thread.IsBackground = true;
thread.Start();
thread.Join(); // optional, if your code should work synchronously
Config Settings (ShellMenu Struct)
The struct accepts one or more of the following configuration settings. Configuration settings are similar in functionality to properties, but they are rarely used. In order to avoid "polluting" the property namespace of the struct, access to these internal properties is provided through the config method.ShellMenu Config Settings
You can use a fixed name when you have some system-global "server" side (e.g., in a system service). Alternatively, you can use a value that include "%1" in it - this "%1" part will be replaced by the session ID. The latter variant is to be used when a server may reside in multiple sessions.
For a client (a proxy DLL), set the value before calling the rmInstall; method (it adds the necessary entries to the registry for the proxy DLL to use them). For a "server" side, you may set the value before activating the struct.
Note that the proxy DLL can connect to only one server, and the value used during the installation of the struct will be used.
This command is executed using the ShellExecute function of the Windows Shell API.
Set this configuration setting before installing the native proxy DLL.
Set this configuration setting before installing the native proxy DLL.
Set this configuration setting before installing the native proxy DLL.
Set this configuration setting before installing the native proxy DLL.
An application may specify just the base name of the sparse package file without processor architecture or extension (a path may be included but not required). The struct attempts to locate the sparse package file by adding the appropriate processor architecture and extension to the base name. When the base name is specified without a path, the sparse package file is looked for in the current directory and in the directory of the application executable (EXE file).
Base Config Settings
- Product: The product the license is for.
- Product Key: The key the license was generated from.
- License Source: Where the license was found (e.g., RuntimeLicense, License File).
- License Type: The type of license installed (e.g., Royalty Free, Single Server).
Trappable Errors (ShellMenu Struct)
ShellMenu Errors
| 2 | An item with given ID cannot be found. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_FILE_NOT_FOUND constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 20 | Cannot load native proxy DLL. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_CANT_LOAD_PROXY constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 28 | The major version of the proxy DLL doesn't match the major version of the .NET assembly. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_PROXY_VERSION_MISMATCH constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 38 | End of data stream has been reached and no data could be read. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_STREAM_EOF constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 55 | Proxy DLL not installed properly. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_NOT_INSTALLED constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 56 | Installation of the native proxy DLL failed. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_INSTALL_FAILED constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 57 | Uninstallation of the native proxy DLL failed. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_UNINSTALL_FAILED constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 58 | Initialization of the native proxy DLL failed. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_INIT_FAILED constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 59 | The current license and the ID in the native proxy DLL name don't match. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_PROXY_NAME_MISMATCH constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 60 | Writing to the Windows registry failed. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_CANT_WRITE_TO_REGISTRY constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 61 | This Menu instance has already been started. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_ALREADY_STARTED constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 62 | A menu item with the same verb is already registered. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_MENU_ITEM_ALREADY_REG constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 63 | No menu items have been registered. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_MENU_ITEM_NOT_REG constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 87 | The passed parameter was not valid. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_INVALID_PARAMETER constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |
| 122 | The provided buffer is too small to accommodate all the data that must be placed in it. The CBFSSHELL_ERR_INSUFFICIENT_BUFFER constant is provided for convenience and may be used in place of the numeric value. |